Like NFS file system, one of the advantage is that EFS can be mounted to different AWS services and accessed from EC2 instances, containers , AWS Lambda functions running within an AWS Region and can be extended to use with on-prem systems as well. You can access EFS file system concurrently from multiple NFS clients.
- When you create an EFS file system using Standard storage classes, you can create a mount target in each availability Zone in the AWS Region.
- When you create an EFS file system using One Zone storage classes, you can create one single mount target that is in the same Availability Zone (AZ) as the file system.
For more information on storage classes, see
Benefits of using EFS Create an EFS File System from AWS Console
- EFS automatically scales the file system storage up or down as per the demand, so applications need not to worry about storage if there is any sudden spike for storage at runtime.
-
On-premise servers and EC2 instances can access EFS, so that it makes it easy to share data between On-prem applications and AWS applications.
EC2 instances can also access EFS file systems located in other AWS regions
through
VPC peering. - EFS is a managed service, so anything related to deployment, fixes and file system management is taken care by AWS.
- Depends on your workload, you can choose either General Purpose mode which supports up to 35,000 IOPS and has the lowest per-operation latency or Max I/O mode which supports 500,000+ IOPS and has higher per-operation latencies when compared to General Purpose mode.
- EFS can encrypt the data 'in transit' (while the data is getting transmitted from source to destination) as well as 'at rest' ( after being copied over to destination).
- From AWS EFS Console, click on Create file system.
- In the next step, from the EFS file system create wizard, if you want to create with default settings, enter below information.

- Name : Give a name to the EFS file system, this is an optional field.
- Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) : Select the VPC where you want to create the EFS file system.
- Storage class : Choose either Standard (stores data redundantly in multiple AZs) or One Zone (stores data within one AZ)
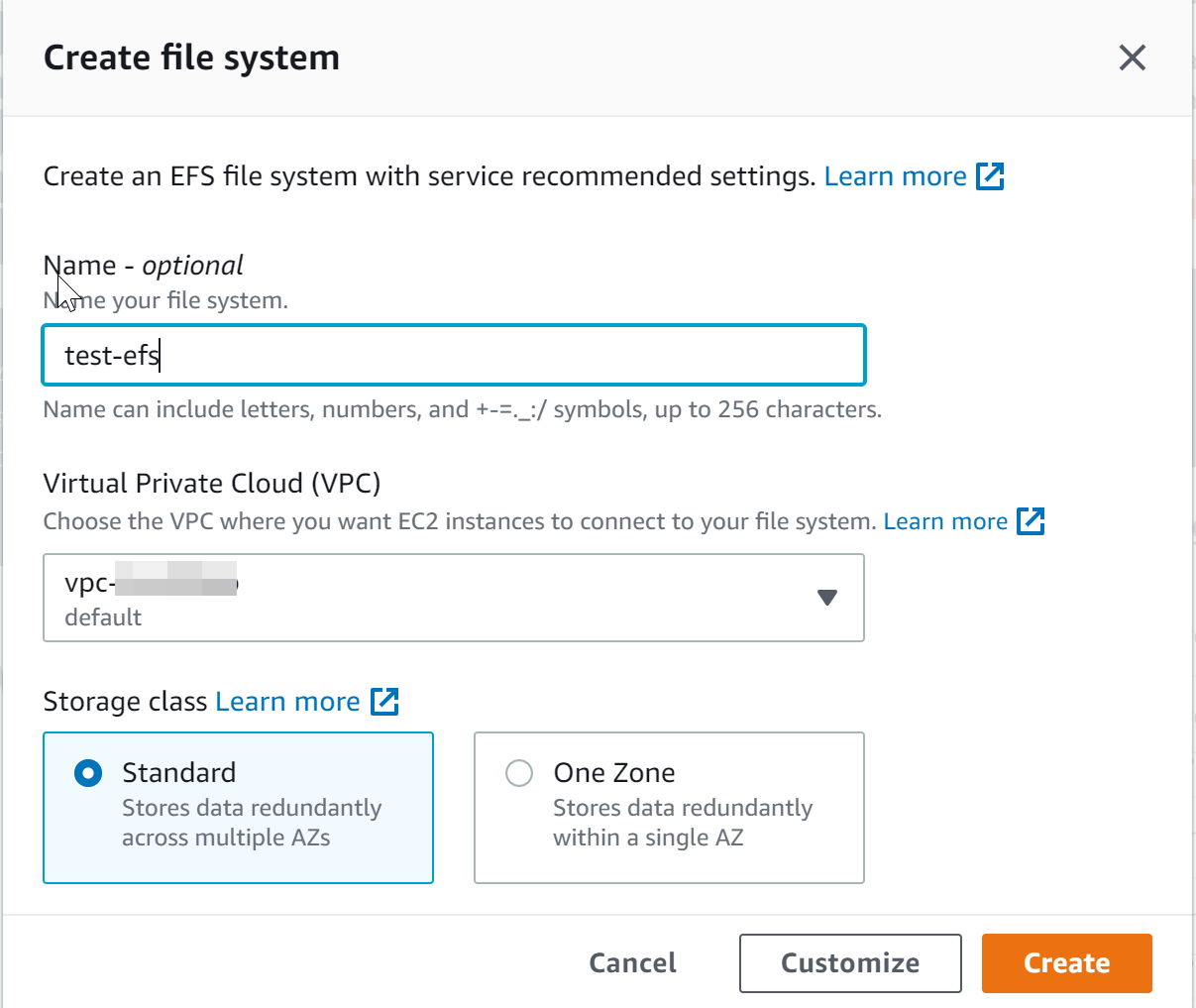
- If you want to customize settings, click on Customize on EFS create wizard and enter below information.
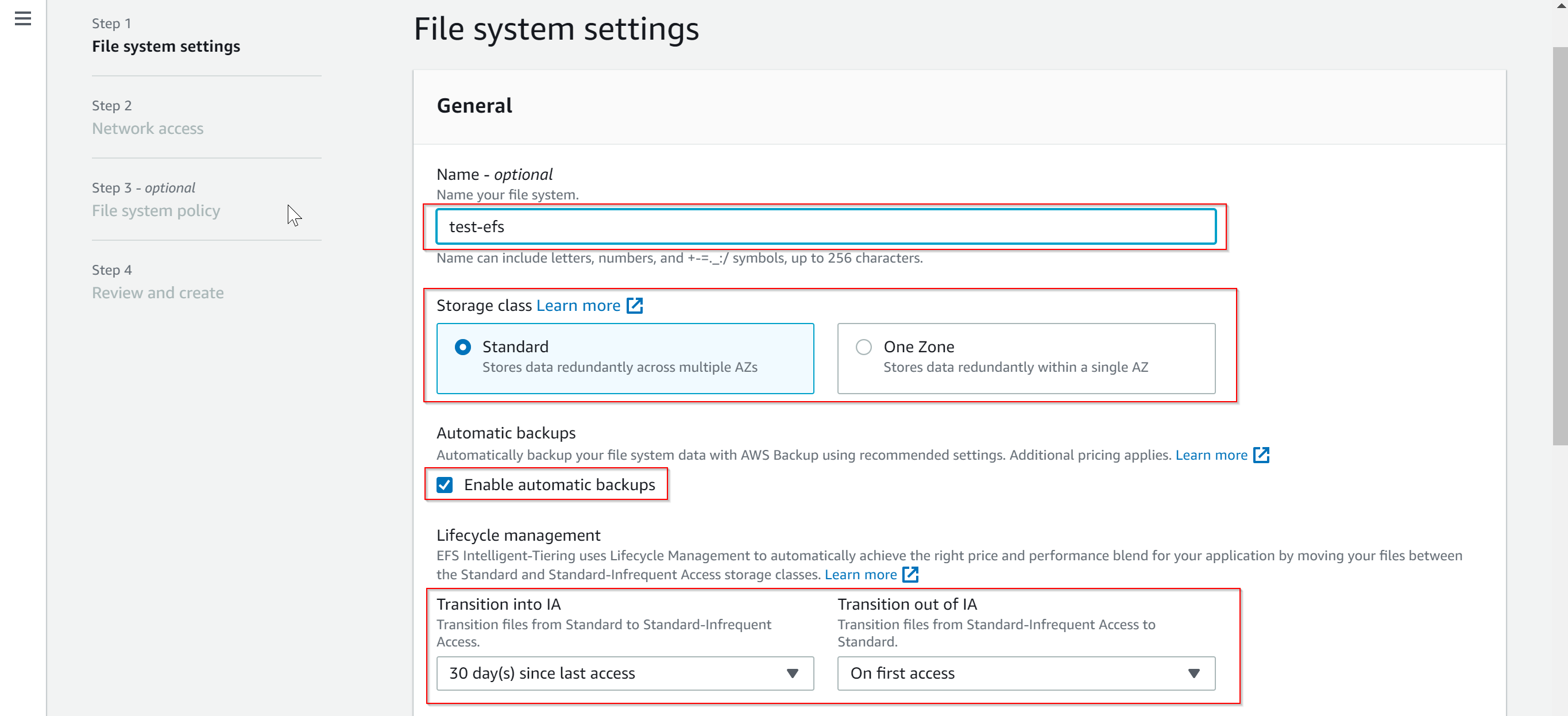
- Name : Give a name to the EFS file system, this is an optional field.
- Storage class : Choose either Standard (stores data redundantly in multiple AZs) or One Zone (stores data within one AZ)
-
Automatic backups : Choose this option if you would like to enable automatic backups of EFS file system.
Once you select this option, you also have to select timeline when the data can be moved to in-frequent access (IA) storage area.
For example if you no longer access a particular file in the last 30 days, so by moving such type of in-frequent accessed data,
this can save some cost on EFS storage.
Also, select on what condition, archived data residing in in-frequent storage area should be moved out of IA storage area, if you need to access this data one off, you can select None or if you required to access the data many times, then you can move it out of IA storage are by selecting On first access.
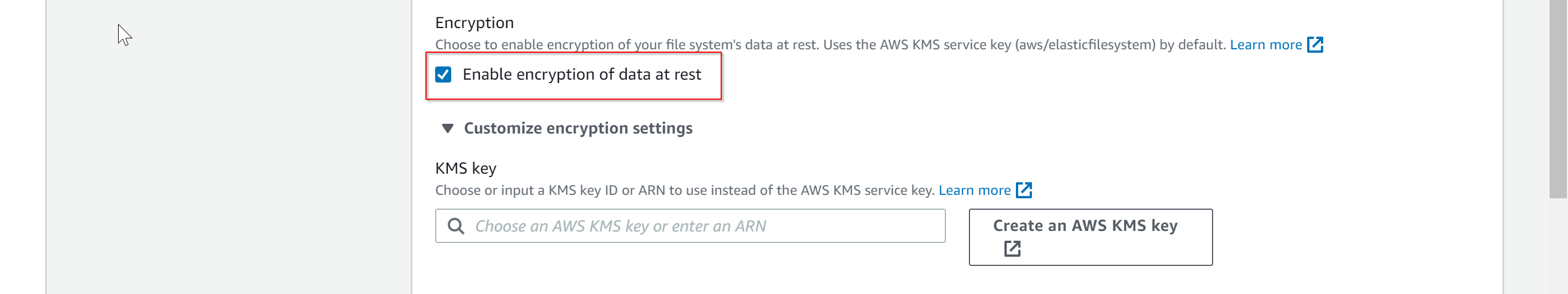
- Next, choose the option whether to encrypt the data at rest or not, if you select this option then the data stored on EFS file system will be encrypted. You have an option to choose your own key from KMS for encryption.
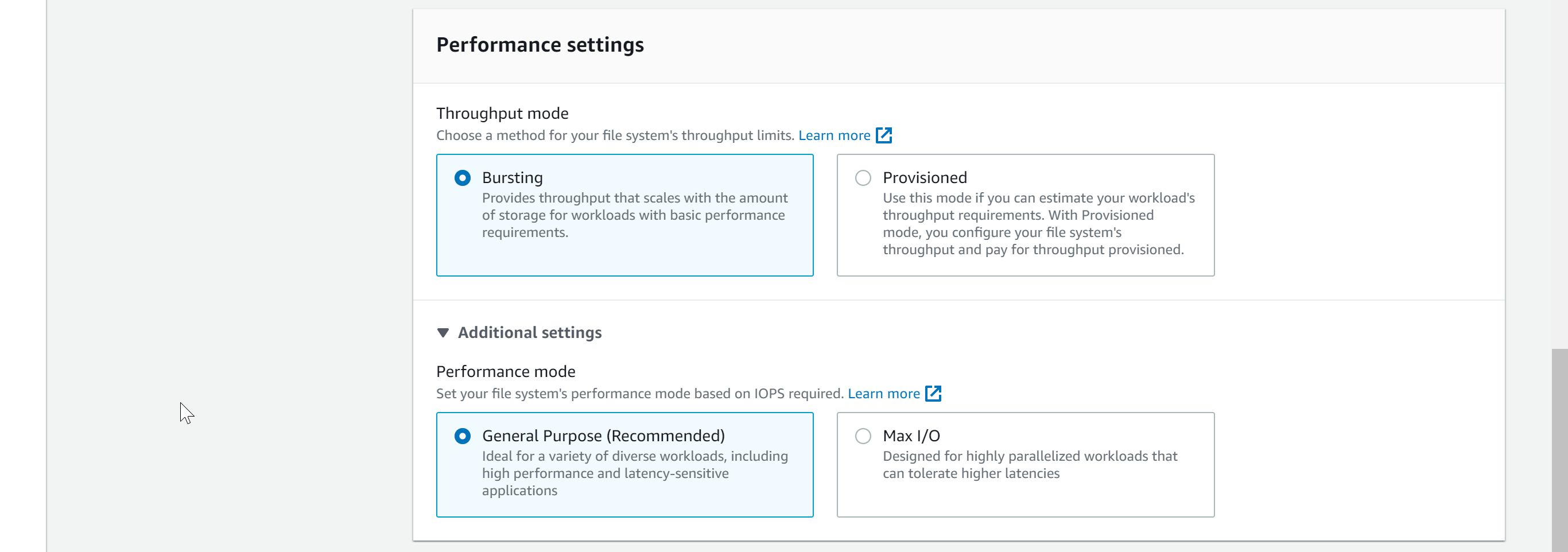
- Under Throughput mode, select throughput mode. Choose Bursting if you want to scale throughput as the data grows with basis performance needs. Choose Provisioned if you already knew an estimate of the workload throughput.
- Under Additional settings, you can select the performance mode that you wish to choose, AWS recommends General purpose for most of the workloads.
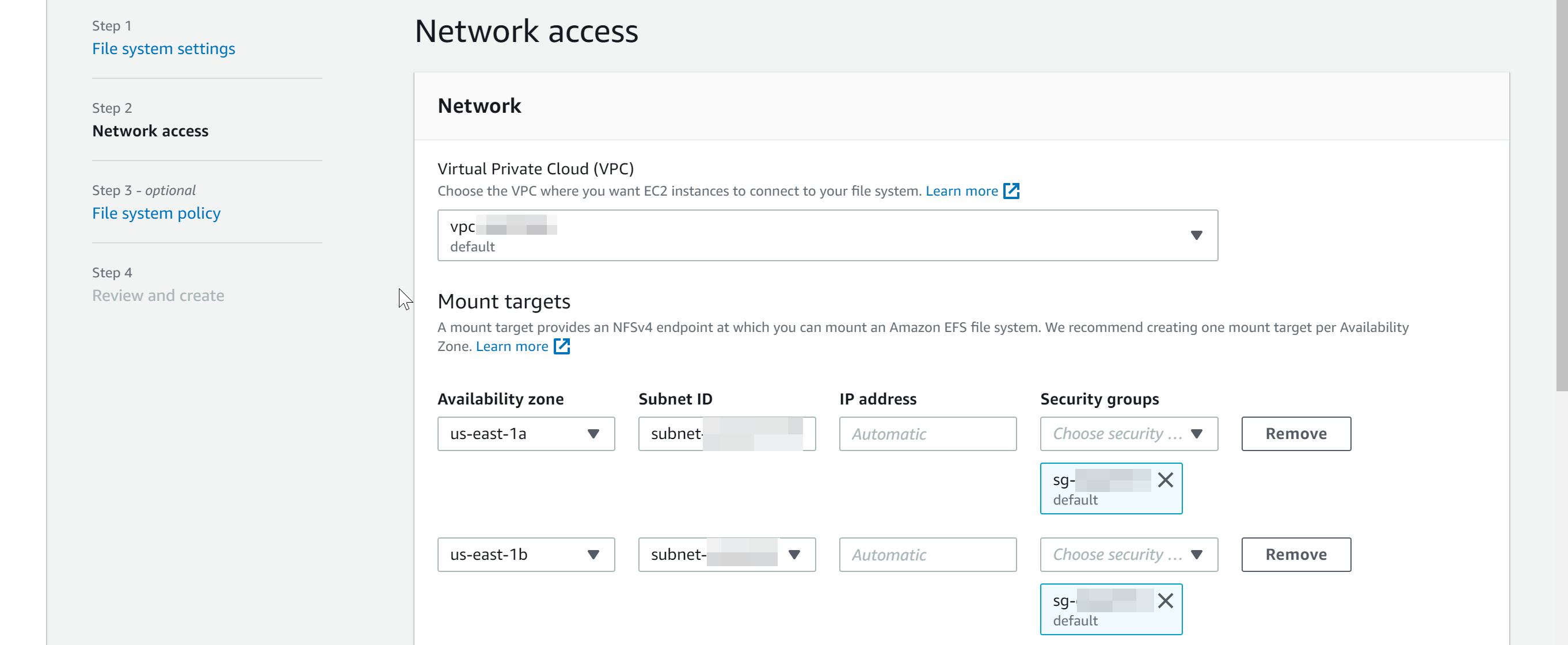
- In the next section, select Network access settings.
- Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) : Select the VPC where you want to create the EFS file system.
- Mount targets : Select mount targets for each Availability Zone (AZ) within your VPC.
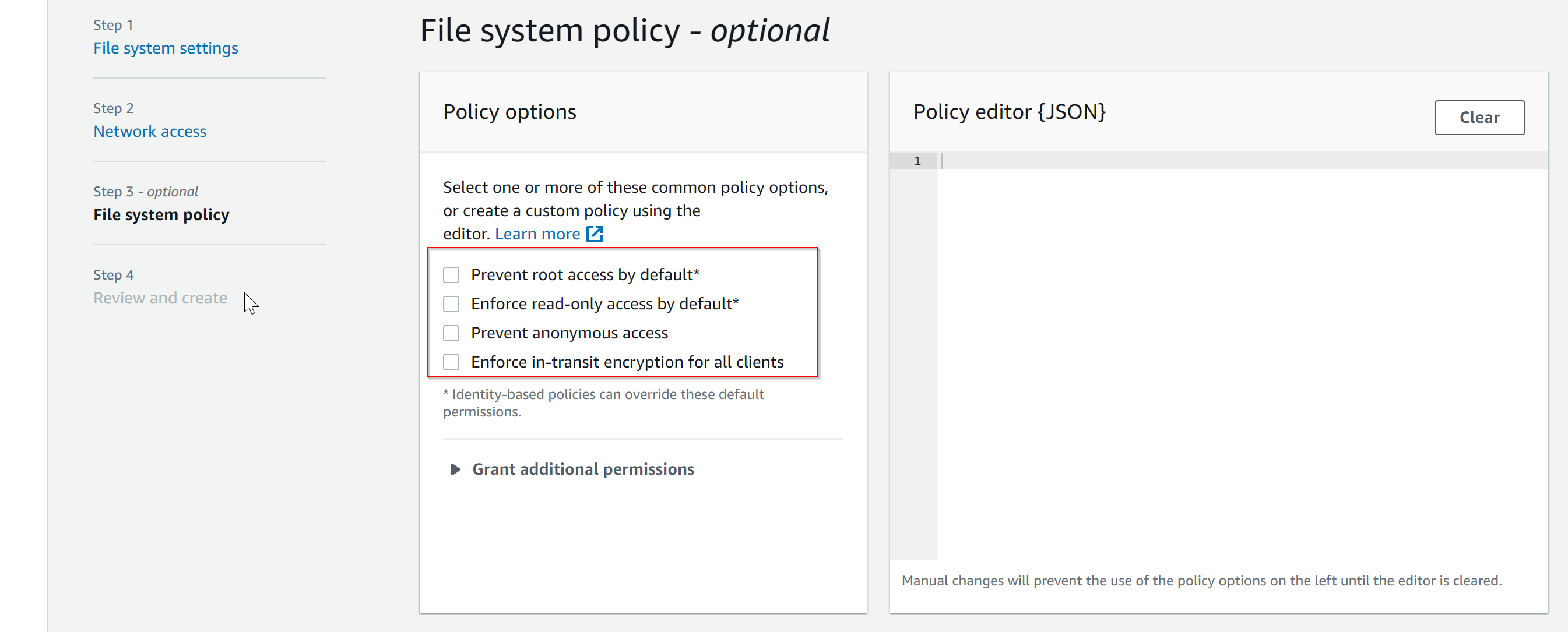
- In the next section, you can set File system policy options, such as prevent root folder access or make the EFS file system as read-only etc. You can select the options from check boxes on left side and the policy JSON will get created automatically.
- In the next section, review all the settings that you have selected and create EFS file system.