EBS volumes are like raw un-formatted device blocks. Once it is attached to EC2, you can create a file system, run a data base etc. EBS volumes are are placed into an AWS Availability Zone (AZ), they are automatically replicated to protect from the failures.
AWS EBS provides range of options you can choose from that suits your business needs. These are categorized into two categories
- SSD backed storage for transactional workloads, such as database and boot volumes, where performance depends primarily on IOPS.
- HDD backed storage for throughput intensive workloads such as logs processing and MapReduce, where performance depends primarily on disk access speed (MB/s).
For more details on types of EBS volumes, pricing and details such as EBS data encryption options can be found here on this page
AWS EBS Snapshots AWS EBS Elastic Volumes
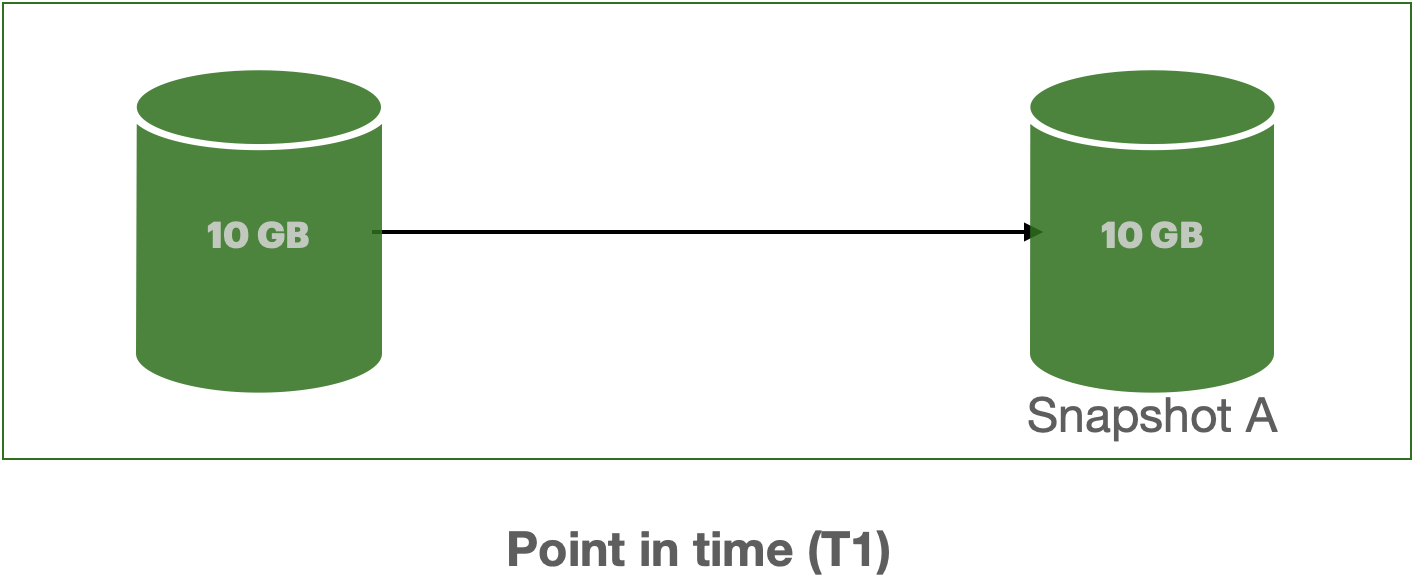
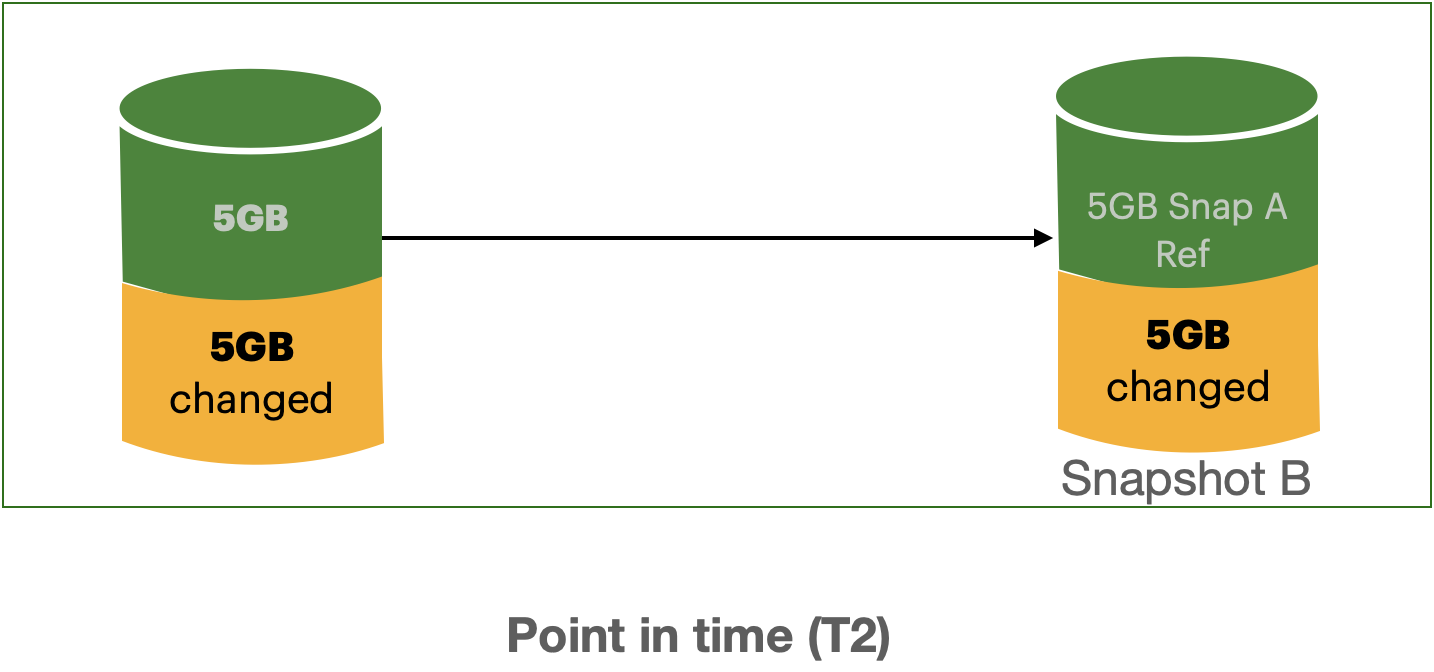
AWS EBS provides a convenient way to save point-in-time snapshots of your volumes to AWS S3. These volumes are stored incrementally, meaning that only the blocks that have changed after your last snapshot are saved. For example if you have a device a with 100 GB of data, but only 5 GB has changed since the last snapshot, then the next snapshot consumes only 5 GB additional data and billed for this additional 5 GB only.
Below image illustrates the how the snapshot looks like point-in-time. As you can see when the Snapshot B has taken, it only takes the changed data and for the unchanged data, it refers from previous snapshot.
Below are some key features of AWS EBS, for full list of features, you can refer to
- When you delete a snapshot, you only remove the snapshot that is not needed by any other snapshots.
- Snapshots can be used to instantiate new multiple new volumes, expand the size of the volume or even move volumes across Availability Zones.
-
You can use
EBS direct APIs for snapshots to read data off snapshots and compare differences between two EBS snapshots. Using EBS direct APIs, you can create EBS snapshots from any block storage data, even if the data resides on-premises and quickly recover into EBS volumes. This feature enables you to achieve disaster recovery goals in AWS. - After a volume is created using an EBS snapshot, there is no need to wait until all the data is transferred from AWS S3 to your EBS volume. EBS snapshots implements a Lazy Loading, so that you can start using the EBS volume right away.
AWS Elastic Volumes feature lets you dynamically increase capacity, tune performance, and change the type the generation volume without any downtime or performance impact. This feature of EBS is useful if your application demands for storage from time to time.
- You can simply create an EBS volume as per today's requirements for your application, knowing that you can modify your volume configuration in future as needed.
- By using AWS CloudWatch with AWS Lambda you can automate volume changes to meet the requirements for your application.